Future of fiber laser welding and cleaning is now.






Meet our products
Let’s meet
FANUCI is an innovative HIGH-TECH company focusing on advanced fiber laser welding and cleaning solutions designated for metal fabrication processes, on the global level.
The company has been growing through the years of experience and development in fiber laser industry with spectacular success. Accomplishing many inventions and over 20 patents, constantly providing meaningful improvements. FANUCI has mastered the core technologies of precision laser welding and cleaning solutions. Our worldwide professional team, highly standardized production and distribution management, as per our company motto, is famously known for its unbeatable quality: Always Chasing for Perfection.
FANUCI already established local 4S centres, service stations and distributors in more than 30 countries. All major components e.g. laser source, laser head, operating system etc. are developed and patented by FANUCI. The remaining parts come directly from world-class suppliers. FANUCI range of products is CE, FDA and TUV certified. Continuously achieving higher standards and faster processing speed.
In 2023 FANUCI transformed to FANUCI GLOBAL GROUP (FGG). Located strategically in 3 core regions, covering the whole world: Asia (CHINA), Europe (POLAND) and America (USA). The company main brands are FANUCI, ULTRON, FANULT designated per unique regions requirements. Providing TOP professional sales&service support with immediate availability of full product range, spare parts and technical knowledge. FGG is firmly committed to continuously improving fiber laser welding and cleaning innovations in metal fabrication industry.
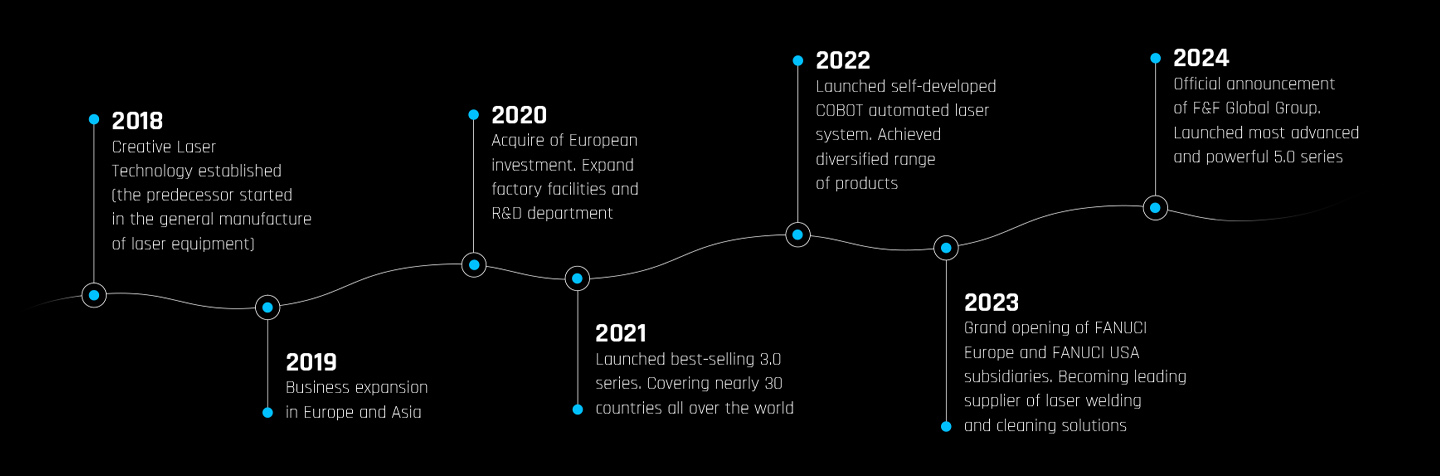
FANUCI chart stages of development
FANUCI Global Group (FGG)
-
FANUCI China
R&D Department, Production&Assembly, Patents, Product supply&service centre in Asia&new developing markets.
-
FANUCI USA
Design development, Quality control, FDA certification, Product supply&service centre in America (North&South).
-
FANUCI Europe
Product supply&service centre in EU, European certification (CE&TUV), Direct cooperation with authorized Distributors in EU.
Why to choose FANUCI?
-
01
Brand General
FANUCI is the most desired brand for laser welding and cleaning equipment internationally.
FANUCI machines are built on top quality, highest performance, and continuous stability. -
02
Parts Storage
FANUCI distribution centres operate in 3 core, strategic regions such as Asia (China), Europe (Poland) and America (USA) which secures the fastest product and service availability worldwide.
-
03
Service Team
FANUCI service ideology is simple. Only an authorized distributors provide local engineers base for appointed territories. This way FANUCI customers are always protected by certified, highly experienced technicians.
-
04
After Sales Support
FANUCI has more than 30 professional exclusive distributors and after-sales points, and growing. Covering most parts of the world, always providing 24/7/365 worry-free support to all customers requiring any service assistance.
-
05
FULL Warranty and Certification
FANUCI machines are always available with FULL 2-year warranty, including all components. And additionally covered with CE, FDA, TUV certification.
-
06
Pioneer in Laser Solutions Provider
FANUCI has already delivered over 2000 machines globally. Securing its position as no1 supplier of fiber laser welding and cleaning technology.
Let’s cooperate
Join our world of the excellent industry products and remarkable services. Would you like to become our distributor and develop your business with FANUCI? If so, please contact us through following contact form at earliest convenience possible.
Why to cooperate with us?
FANUCI maintains, at all times, high numbers of in-stock laser welding and cleaning machines to provide customers with the fastest supply chain possible. Every in-stock equipment has completed full, rigorous FAT testing at the factory to ensure delivery speed without any lacking of our consistent, high standards for sales quality. All FANUCI machines comply with the highest standards based on required certification accordingly to market requirements e.g. CE, FDA and TUV certificates.
FANUCI maintains, at all times, full spectrum of all parts required for servicing to provide customers with the fastest technical assistance possible. Every in-stock part has completed full, rigorous FAT testing at the factory to ensure the quickest delivery without any lacking of our consistent standards for service experience quality.
FANUCI provides, at all times, fully trained and experienced engineers for technology introduction and training purposes to provide customers with fastest technical advice and upgrades possible. Available online and directly at the chosen production sites.
FANUCI is constantly looking for fiber laser technology expansion that allows our business associates to explore their markets in position of the most professional, reliable and trusted laser welding and cleaning suppliers. FANUCI machines can always be pre-tested in designated areas. Presentations are being held in main FGG locations, showrooms of our distributors or through demo-cars being on the move 24/7.
